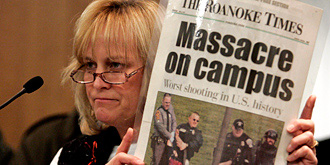The suspect in the Minneapolis church shooting followed by a manifesto against children, transgender people, Jews, and others. The mass shooting at Annunciation Catholic Church was described as an act of domestic terrorism. In this case the violence culminated in two fatalities and 18 wounded. Terrorism requires an intent to bring chaos and death to a mass society – in this case children praying at mass during a catholic school’s opening day of school. The FBI says the events was targeted against the Catholic school. The gunman fired their rifle at children and worshipers sitting in the Annunciation Catholic church during mass. Chief O’Hara at Minneapolis Police called it senseless and a deliberate act of cowardice beyond comprehension.
Police
LODD – Unsustainable pain in the thin blue line

I recently read an article in the Washington Post first published in 2018 written by Michael Miller. I sent him a note suggesting he pick up the ball on this. I am interested in the topic of police behavioral health and understand the dynamic of law enforcement suicide and how the notion remains stuck in modern police service due to stigma with suicide and mental health wellness in police officers. I am a former police officer and know there is nothing more horrific than a police officer suicide or death to a member. In Chicago officers have taken their own lives while in the driveway of their duty station. In Los Angeles, four active duty or retired officers committed suicide in one weekend in November 2023. In Washington DC, an officer who was ordered back to work following the attack on the Capitol killed himself while driving to his work. People are starting to connect years of service with risk for suicide and many departments are taking police officer wellness as the key to both career hardiness and job performance. One officer granted LODD status remains in conflict. Erin Smith wants her husband’s name added to the D.C. police department’s list of fallen officers and engraved on the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial, and the official burial honors traditionally afforded to officers killed in the line of duty according to a Washington Post opinion piece from .
I was part of a panel about police suicide in Chicago in 2019. The dark problem is especially taboo when cops are involved in a line of duty shooting and later kill themselves. The Chicago program was held following a rash of suicide deaths in the Chicago PD. Most officers do not return to the job following the investigation of their actions. Some do. Those who do return are off the job within five years. I am a police consulting psychologist in the Boston area. I am charged with pre-employment screening and fitness for duty exams after law enforcement exposure to trauma. More needs to be done to link on-the-job exposure to horrific and despicable human behavior to suicide and afford them line of duty death status including the honors and pension compensation just like other officers who die in the line of duty. In Washington DC officers who took their own lives following the Capitol insurrection were afforded line of duty status. Why not others?
“Police work took officers to “some of the darkest places in America,” he said, and few were darker than the scenes of officer-involved shootings, often called “critical incidents.” Line of duty death and police well-being are strongly impacted. Some police officers kill themselves after critical incidents they cannot unsee.”
“Chicago is kind of like ground zero with the number of suicides that are happening on a monthly basis now at this point,” said Daniel Hollar, who chairs the department of behavior and social science studies at Bethune-Cookman University in Florida. Dr Holler hosted Dr Doug Joiner to Chicago for a symposium in 2019. Dr Joiner taught us much of why officers kill themselves. He says they become embittered, they feel a deep sense of thwarted belongingness and grow increasingly detached with higher risk of suicide. “These are police officers answering calls of duty to protect lives. We (need to) do our job to make their jobs safer.” said Dr. Joiner. After an officer suicide, personnel try to reconstruct what was going on in the person’s mind by systematically asking a set of questions, in a consistent format, to the people with the greatest insights into the person’s life and mind—family, co-workers, and friends.” This is known as a psychological autopsy, and I have proposed it for any officer who dies by suicide. If this is done effectively, I can assure you there will be no escalation of suicide among police officers. Something police chiefs and city counselors unfairly fear.
I am working with one department where two officers have not returned to active duty nearly two years after being involved in a violent shooting while trying to help someone who had led them on a chase ending in a roll over motor vehicle crash. As officers approach the overturned vehicle the driver began shooting at them with a semiautomatic rifle. These brave men were traumatized by the fatal shooting of a subject who first fled from a legal police car stop and then opened fire on them. They have been out of work on administrative leave receiving behavioral health support but are unlikely to return to service.
I have conducted a psychological autopsy on a police constable who was involved in a line of duty shooting resulting in death in November 1971. He was a full-time police officer in Mifflin Township, OH that had no formal police department. No chief and no field training support. He shot and killed a man and was cleared of wrongdoing. Sadly, he killed himself in front of his wife one year later at Christmas. He grew restless and embittered after being villified by people inhis community. He believed nothing was being done to support and protect him. He is buried in a cemetery near the man he shot and killed. I want this death changed to line of duty (LODD). Why? When someone kills themselves most departments, including all smaller agencies, fail to discover the set of facts and red flags left behind leading to suicide. The investigation is often cursory, purportedly out of respect to the family. But there are factors in the careers of police officers that make them at higher risk for suicide then the public. This is not sustainable.
I have been writing about this for 9 years in the pages of my human behavior blog. In Chicago, if an officer comes forward looking for help, they are stripped of their firearm, police powers, and their star (badge). This is demoralizing according to officers I have spoken to. Why would anyone come forward if this is the protocol. This may be changing, whereas CPD has added therapists in each of their 23 police stations. Unfortunately, one cannot unsee some of the darkest scenes in human behavior like the death of a law enforcement officer or domestic violence resulting in death. The psychological autopsy must include a 3-month list of calls the decedent answered including those for which he or she was given debriefing, defusing, or time off for respite from the job. I would want to understand how the call volume may have triggered underlying acute stress of new calls that triggered new trauma? In any case, the story was interesting and careful analysis is important in all incidents resulting in police suicide.
Finding purpose for career success
As a member of the Direct Decision Institute, Inc in Worcester, Massachusetts, my colleague Dr. Leo Polizoti, the Institutes senior lead psychologist, are charged with doing pre-employment psychological screening for all officers heading to a regional police academy across New England. There are details about the pre-employment process at the institute website: drdecision.org. One question I usually ask is: “Why do you want to be a police officer?” As you might expect, the answers are all well-rehearsed and touch on inspiring, decorated family members who were police officers, the personal desire to help people, or a memorable encounter with a member of law enforcement early in life. There are always others too.
A more curious inquiry might sound like this: “why would you want to be exposed to fatal car crashes, domestic violence, including intimate partner homicide, completed suicide and suicidal persons, sudden infant death, violent, intoxicated subjects, random citizen complaints, professional jealousy, long hours, and sometimes decrepit leadership?” I might even add: “if you want to help people why not become a nurse or high school teacher?”
As a police consulting psychologist my goal is to offer my best judgment about candidates for police officer. I offer my two cents worth of resiliency advice by painting a portrait of how they see themselves five years in the future. When asked what they expected in the pre-employment psychological interviews one or two have said it was a “waste of time.” Now these men and women are in the minority, only 1 in 15 has said that in my last round of interviews. But just as importantly, going forward, these new officers are going to represent law enforcement and should be better prepared to embrace mental health awareness and the reduced stigma associated with behavioral health and human resilience. Most police officers are starting to understand this. To say that a one-hour meeting with the police psychologist was a “waste of time” reflects both the lack of understanding of personal wellbeing and a blind spot in progressive policing. Mental health services is everywhere in law enforcement on both sides of the badge.
Law Enforcement and the “window” of attack against domestic violence
Human Behavior blog
In Iceland, the first 24 hours after a report of domestic violence, the window of opportunity is open. During this window there is multidisciplinary response from police, social work, legal experts, and from the child protective service that establishes a safety plan and targets supporting the victim from her household, and sometimes away from the dangerous intimate partner.The first 24 hours after the report comes in is critical. Victims are more likely to accept help if definitive, comprehensive assistance can be offered right away. Within the window of emotional opportunity.
The Iceland Project puts together the package needed to bring charges by having a team of social service and law enforcement investigators who work together during the “call out”. One reason cases of domestic abuse seldom make it to court is because days and days go by before investigators can interview the victims. Some go to work, and some do not make themselves available to officers. “In Iceland, twice as many women are reporting incidents of domestic violence to the police than they were two years ago. This is due to an ongoing police initiative to provide women with better-timed and better-located assistance, which is bringing the problem out of the shadows” as reported in apolitical in 2017. I have called for regular aftermath follow-up in cases of domestic violence as a form of community policing. Officers work in pairs and stop during the next day to complete a check-in. Victims are contacted by their abusers or the family of the abuser or may be harassed via social media and made to feel like it is their fault this occurred. I had one victim tell me she was beaten up by her husband because the dinner she had prepared was late and unsatisfactory. I stayed in contact with her until the family quickly sold their home and moved from the area. That is pretty typical whereas the abusive partner wants to keep his wife under control. As soon as she makes friends he moves her somewhere else. Even if he takes a different job. Cases of domestic violence here in the United States skyrocketed during the pandemic quarantine that also gave birth to new higher rates of substance abuse and changes in behavioral health and well-being.
Police in Reykjavik, Iceland believe that detectives or senior police officers must intervene within the window – 24 hours from start of a call out, to put together a strong case and collect evidence. They work in teams of 4 or 5. The former protocol was often several days after the call and coincided with the honeymoon period. Bail conditions frequently fail DV victims as the abuser is often bailed out within 1-2 hours. Egregious cases of DV should be held without bail until a dangerousness hearing may be initiated. The result of this usually resulted in cases being dropped and victims staying in dangerous relationships. In theory, victims are more likely to accept support and provide meaningful evidence in the first 24 hours after their abuse. The window program is designed to link victims with programs such as housing, psychotherapy, job assistance, and financial means for a new start.
The Iceland Window Project also offers perpetrators the same assistance and supports that victims receive. Charges against perpetrators of abuse have gone from approximately 24 percent of cases to approximately 30 percent of cases. This is a modest improvement at best, according to the BBC podcast People Fixing the World who report that caseloads have increased dramatically since 2014. In spite of modest changes in prosecution numbers the Window Project’s fundamental aim is to reduce intimate partner abuse. It is a well designed project to support victims and keep them focused on the problem. Many practitioners believe that when a family is in crisis, such as when police are called to the residence, that great change is possible. There has been some movement toward prosecuting abusers even when the victim changes her mind. This is a primary reason for the Window Project’s success. By getting statements, photos, and other evidence there is greater likelihood that cases can go to court even when the victim chooses not to prosecute police are now doing this on behalf of bullied partner/victims. Children who are exposed to severe domestic violence are more likely to go on and become victims going forward. Or worse, they grow up and do exactly what their abuser did.
Here in the United States victims of domestic abuse are at great risk. Especially as they prepare to leave their abusive partners. Law enforcement is required to arrest perpetrators of DV whenever signs of physical trauma. That is generally understood by the police and the abusive spouses. But what happens just as frequently, law enforcement officers send the abuser away for the night or weekend. This makes things worse for victims and children.
The domestic killing of another Gabby Petito: Send me dead flowers and I won’t forget to put roses on your grave

By all appearances Gabby was a smart and loving companion. She wanted to impart her love for Brian Laundrie and the life she hoped they would have together using social media. They were engaged to be married but this would never occur. Now she is the victim of homicide. “The loneliest time in a life is being in the wilderness in the middle of night, with a person you once loved, now killing you. “If you scream for help in the wilderness and there is no one there to hear it except your killer, was there ever really a scream?”” Personal correspondence from B.F. Gagan. New website: http://www.arrestbrianlaundrie.com for details on the $25,000 reward for finding Brian Laundrie. Details on the site. There have been at least 11 questionable tips transmitted to the FBI tip line as of October 4, 2021. The media reports keep Laundrie’s picture in the news cycle. Just today someone reported seeing him on the Appalachian Trail where hikers go from Northern Georgia and finish at Mount Katahdin – the highest peak in Maine. Mr. Laundrie has done parts of the trail and is familiar with its isolation from society. He may feel that he can make a safe getaway while remaining off the grid. But someone recognized him today in South Carolina. Or a look alike.Gabby Pitito is a case study for intimate partner abuse. From the outside, we saw a beautiful couple enjoying the wonders of the American West. Social media accounts updated with regularity bringing hundred or even thousands of likes. Gabby had a gift for creating an image. Only now have we learned the imagery was deeply flawed. Friends of the pair described Brian Laundrie as a jealous and controlling partner as described by Rose Davis, a friend of Gabby Petito. Common among abusive partners is separating intended victims from their emotional support systems leaving them isolated and without friends and needed help. It is a common red flag in most cases of domestic abuse and more commonly, domestic violence homicide. In most cases the abuser has an underlying pathological jealousy and in some cases, delusions of his partner “hooking up” with someone whenever she is out of his site. Once while on duty with the police agency for whom I served, a jealous husband came crashing into town hall hoping to catch his wife in a tawdry affair while she stood in line to cast her vote in a 2015 election. He had been sending her text messages from the parking lot like “Where are you? Who are you with?” Ultimately, the man needed an escort out of the building and was given a trespass warning. For her part, she felt pangs of guilt, resentment, and fear for keeping him waiting. Shortly after Election Day the family moved away from town. It happens all the time.
Women are kept from seeing friends and family members in an effort to disempower them of any sense of self. We now know this got worse during the pandemic where people were isolated anyway and those living in domestic fear became further inhibited and marginalized. By outward appearance Gabby Petito was terrified of her boyfriend at the time they were stopped in Moab, UT. This behavior speaks volumes about the state of the relationship just as Supervisory Agent Melissa Hulls said after they encountered Gabby and boy friend Brian Laundrie in late August 2021. I have reached out to Supervisory Ranger Hulls on two occasions without hearing back. I am interested in hearing from few friends of Gabby Petito with their appraisal of what they saw happening to the couple during pandemic? The pair had been together over 2 years and managed to get through waves of pandemic only to be set free on the cross country junket. Both seemed physically fit and healthy. Had the pandemic and subsequent quarantine changed them in any way? How did the couple decide to embark on this journey? Whose idea was it? “Brian has a jealousy issue,” Rose Davis of Sarasota, FL said in the September 17, 2021 New York Post article. “I’m her only friend in Florida to my knowledge and that’s not because she can’t make friends, he just didn’t want her to have friends.”“You can’t say that nothing can be done, because nothing will be done,” said Michael Sefton, a former Westbrook police officer who now works in Massachusetts and retired from the the New Braintree Police Department.


Officer distress in Bangkok, Thailand
“Today police morale and emotional health have hit rock bottom, he said, because of a number of factors, including botched policy-making when it comes to their career path that doesn’t take into consideration the officer’s needs and desires.” Bangkok Post December, 2019

And the year 2020 was not any better and very likely triggered added stress and tension among the working wounded in Bangkok and beyond. Shortly after I visited Bangkok, in early 2020 a member of Thai Army service in the Northern Province went off and killed his superior officer and over 20 people in his community. Very rare in the Thai history. My former Chief and I had met another commander from the Northern Province detail and liked him a lot. He smiled and seemed confident before returning to the Northern Province. Gun violence in Asia is rare and mass shootings are more rare still.
Next came the virus. Thailand got out in front of the contagion and closed things down and required both social distancing and masks. The total number of cases per 100,000 souls is much less than here and most other places.
Meanwhile, Thailand is offering a softer, gentler service to those officers who sign on to be law enforcement officers trying to accommodate the needs of the police service.
The Field Training Officer: Important things they may not know
Most departments has active field training protocols that recruits must pass after leaving the academy. This means they ride along with the FTO until they are ready to function independently as LEO’s. The specific time line for this depends on FTO daily observation reports during the phases of field training. These begin with close supervision where the trainee does little of the daily work. In the latter phase of training the FTO may pull back and provide intervention only if needed by allowing the trainee to be the lead on all calls.
Officer resilience depends upon solid field training with adequate preparation for tactical encounters, legal and moral dilemmas, and mentoring for long-term physical and mental health. Michael Sefton, Ph.D. 2018
Law enforcement officers begin their careers with all the piss and vinegar of a first round draft pick. This needs to be shaped by supervised field training and inevitably will be effected by the calls for service each officer takes during his nightly tour of duty. Much like competitive athletes, law enforcement officers at all levels exhibit “raw” talents, including leadership abilities and the cognitive skills to go along with them. Moreover, like competitive athletes, these raw abilities have to be honed, refined and advanced through a combination of modeling, coaching and experience in order for the officer to develop the skills needed to improve performance, as well as prepare them for career advancement according to Mike Walker. This important task falls upon the field training officer (FTO) and is a critical phase in probationary police officer’s development. “The FTO is a powerful figure in the learning process of behavior among newly minted police officers and it is likely that this process has consequences not only for the trainee but for future generations of police officers” according to Caldero and Crank (2011). In 1931 the Wickersham Commission found over 80 percent of law enforcement agencies had no formal field training protocols for new officers entering the field of police work described by McCampbell (1987). In 1972, formalized field training protocols were introduced by the San Jose, CA police department that became a national model for post academy probationary field training.
Just before I was promoted to sergeant while working for a law enforcement agency, USCG Vice Admiral John Currier, a friend of mine said to me: “Michael, move up or move out”. I wasn’t sure what he meant by that but given my 9 years as a patrolman, I started to lobby for a promotion to sergeant. The agency at which I worked had little turnover in the middle ranks so I was never sure I would get a chance for promotion.
All law enforcement officers should have a career path when they graduate the academy that lays out a career path based on officer interest, career improvement goals, on-going training interests, and agency needs. Training opportunities offer new officers the chance to gain experience in anything from specialized investigations i.e. sexual assault and child abuse, firearms instructor, domestic violence risk assessment to bike patrol and search and rescue. Our chief believed strongly in incident command, active shooter response, and emergency medical technician training. I went on to take the paramedic technician course at a local college in 2011-2012. In many ways my former agency was well ahead of the curve in training opportunities and tactics including use of body worn video cameras, taser training, stop sticks, and individually deployed patrol rifles. I was encouraged by my chief to participate in a research opportunity I was offered in domestic violence homicide from a case in northern Maine, a community much like the one I served. From this research we introduced a risk assessment instrument developed by Jacquelyn Campbell.
The chrysalis for me came in August, 2012 when I was appointed by the Select Board to sergeant at the recommendation of my chief. Before this could occur, I had put in a significant amount of time developing a field training program, domestic violence awareness and lethality assessment protocols, and police-mental health encounter training. I learned the hard way that most police officers do not like working with citizens with mental illness and hate attending training classes on mental health awareness and crisis intervention training. I realized that I needed to become a leader and in order to do so I needed to become better in communicating with the troops and with those up the chain of command. In order to develop leadership I was sent to sergeants school but what I learned was the importance of being a role model for those in training and to teach by doing, teach by example. I also learned that field training is demanding, exhausting work if done with the precision needed to fully socialize the trainee and provide needed modeling while gradually offering greater independence for the trainee.
 Field training involves months of practicing ‘what if‘ scenarios, learning the ropes of the police service, use of force, and writing reports. Early in the phase of training the tough discretionary decisions faced by a probationary officer are made by the senior training officer based on prior judgement, experience and what is most prudent for the specific incident and conditions on the ground. “Agencies should thus maintain a greater degree of FTO supervision, not just trainee supervision. Such an effort would go a long way toward improving FTO programming and better informing the needed research base” Getty et al. (2014, pg. 16). Field training is often time limited with special consideration for officers who need additional training in specific skills or personal areas of concern. Some officers are put on career improvement plans and extended field training, when needed, and some probationers are discharged from the agency because of skills or behavior that are not compatible with police work. Law enforcement agencies want active police officers who represent the core beliefs of the agency and individual community needs.
Field training involves months of practicing ‘what if‘ scenarios, learning the ropes of the police service, use of force, and writing reports. Early in the phase of training the tough discretionary decisions faced by a probationary officer are made by the senior training officer based on prior judgement, experience and what is most prudent for the specific incident and conditions on the ground. “Agencies should thus maintain a greater degree of FTO supervision, not just trainee supervision. Such an effort would go a long way toward improving FTO programming and better informing the needed research base” Getty et al. (2014, pg. 16). Field training is often time limited with special consideration for officers who need additional training in specific skills or personal areas of concern. Some officers are put on career improvement plans and extended field training, when needed, and some probationers are discharged from the agency because of skills or behavior that are not compatible with police work. Law enforcement agencies want active police officers who represent the core beliefs of the agency and individual community needs.
Field training has perhaps the most potential to influence officer behavior because of its proximity to the “real” job according to Getty, Worrall, and Morris (2014).
Probationary officers can be taught the how and when of effecting an arrest but the intangible discretionary education comes from FTO guidance and socialization that takes place during the FTO training period. Research has revealed that officers’ occupational outlooks and working styles are affected more by their FTOs than formal “book” training, Fielding, 1988. The selection of who becomes an FTO is not well defined. In a study at Dallas PD probationary trainees were exposed to multiple FTOs over 4 phases (Getty et al. 2014). The study revealed a correlation between new officer behavior – in the 24 months after supervision, as measured by citizen complaints and the FTO group to whom they were assigned. It is conceivable that the results in the study may be due to the relative brevity of training at each phase may have stopped short of instilling good habits or extinguishing bad habits in many new police officers. I have worked in agencies where only the sergeants were the FTO’s by virtue of rank and supervisory acumen long before systematic field training programs were introduced. In Dallas, results showing officer misconduct via high citizen complaints may too have been associated with unprepared FTO’s who were drafted to supervise the trainee and who were not prepared for that role.
“Bad apple” and/or poorly trained FTOs may thus have a harmful influence on their trainees. Getty et al. (2014)
Choosing successful FTO’s is of critical importance for new officer development and for future generations of law enforcement officers. The values espoused by the FTO have enormous impact on the behavior, habits, and professionalism of new police officers. It has been shown that the quality of this training belies post-supervision job behavior and success. Haberfeld (2013) has offered a supportive assessment of the assessment center approach to FTO selection suggesting there are qualities that may be quantified in the selection process. This may be helpful in the selection of FTO’s who are professionally resilient and emotionally hardy as they lead the new probationary officer into his career. If officers are randomly assigned to provide field training without forewarning or preparation this may staunch career growth in the probationary LEO. If this becomes the norm then FTO’s may have provide more of what probationary officers need such as correct values, discretionary wisdom, and perhaps less negative socialization that can lead to embitterment, misconduct, and citizen complaints.
At times of high officer stress when high lethality/high acuity calls are taken the probationary LEO is apt to require greater support and guidance from the FTO. It is during these critical incidents that post hoc peer support and defusing may take place. Training LEO’s should be permitted to openly discuss and express the impressions they experience to calls that may be more violent, and outside of the daily norm for what he or she has been doing. In doing so, the impact of these high stress exposures may be mitigated and emotional resilience may germinate. The responsibility of FTO’s to reassure and invigorate trainee coping skill and mindful processing of critical incidents cannot be under emphasized. FTO’s understand that healthy police officers must be permitted to express horror when something is horrible and feel sadness when something leaves a mark. They will become better equipped in the long run if allowed to fully appreciate the emotional impact that calls for service will elicit in them. The stigma of high reactive emotions from high stress incidents, i.e. homicide or suicide, is reduced when officer share the call narrative and its allow for its normal human response.
Michael Sefton, Ph.D.
2019
REFERENCES
Caldero, M. A., & Crank, J. P. (2011). Police ethics: The corruption of noble cause (3rd ed.). Burlington, MA: Anderson.
Fielding, N. G. (1988). Competence and culture in the police. Sociology, 22, 45-64.
Getty, R, Worrall, J, Morris, R. (2014) How Far From the Tree Does the Apple Fall? Field Training Officers, Their Trainees, and Allegations of Misconduct. Crime and Delinquency, DOI: 10.1177/0011128714545829, 1-19.
Haberfeld, M. R. (2013). Critical issues in police training (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
McCambell, M. Field Training for Police Officers: The State of the Art (1987). DOJ: NIJ, April.
Police officer vulnerability previously ignored, hidden from plain site
What is currently understood as repeated exposure to trauma and its emotional impact was once thought to be a testament to toughness invoking the specter of a wall of silence. Law enforcement and first responder suicide has increased over the past several years and now exceeds the number of LEO’s killed in the line of duty. Why are cops choosing to take their lives? This is especially felt in Chicago where seven officers have taken their own lives in the last 8 months. In more than one case an officer committed suicide in the police vehicle or in the police department parking lot.
My colleague Dr. Leo Polizoti, Police Consulting Psychologist at the Direct Decision Institute, Inc. has been active in law enforcement training, fitness, and prescreening for over 40 years. He served over 30 agencies across New England and provides supportive psychotherapy as needed.
Dr Polizoti and I were recently involved in a symposium on Police Suicide in Chicago sponsored by Daninger Solutions from Daytona Beach, Florida. Among the presenters were Dr Thomas Joiner from the University of Miami, recognized expert in suicide, police sergeant Mark Debona from Orlando, Florida and Dr Daniel Hollar, Chairman in department of Behavior Science at Berthune-Cookman University in Tallahassee, Florida and CEO at Daninger Solutions.
There are many reasons why police officers have an increased levels of depression and stress. Most are associated with repeated exposure to traumatic events like exposure to dead bodies, violence, childhood injury or death, terrorism, fatal car crashes, and more. Most officers are able to remain professionally hearty when provided the opportunity to defuse the exposure soon after an incident. Career performance should include reducing officer depression and embitterment by building resilience starting in the academy and lasting throughout an LEO’s career.
The Mind-Body connection is well established and the role of stress in LEO career well-being is becoming a agency focus beginning in the academy.
“Not only must we as negotiators learn to take care of ourselves emotionally and physically – we must also be prepared to intervene with an actively suicidal officer. “
Dave DeMarco FOX News Kansas City
Is it any wonder officers lose hope and resilience. There are inherent risks that LEO’s assume when they sign on like forced overtime, changing shifts, off-duty court appearances, the chance they may become injured, disabled or killed while serving the community. There are also systemic stressors like supervisory bullying, professional jealousy, lack of opportunity to have an impact on policy, career stagnation, and paramilitary chain of command that often devalues education and innovation. Agencies are beginning to track exposure to trauma and its correlated change police officer resilience in real time.
In Worcester, Massachusetts, LEO’s are required to attend defusing sessions following high lethality/high acuity exposure. These sessions are kept private from members of the command staff and records are saved by the police consulting psychologist. The department has nearly 500 officers who are paid for their participation when they attend. It has been proposed that officers undergo annual “wellness checks” as a routine in some agencies such as KCMO. I have proposed a system of tracking officer call acuity and invoking mandated behavioral health assessment after a specified number of high acuity/high lethality calls for service. This is one way of reducing the stigma that officers face when they are sent for “fitness” evaluation or any sort of behavioral health care. The stigma associated with mental health may be reduced by having specified referrals following identified high profile incidents. Officers may be considered to be getting peak performance training at these defusing sessions as they are designed for enhancing officer awareness and reducing the human stress response.
Now, the KCMO department has mandated yearly wellness exams for officers in certain units like homicide and those dealing with child abuse. This was initiated to decrease the impact of traumatic events on police officer well-being. Officers at KCMO can also get up to six free anonymous visits to a mental health clinician each year, and the department has a peer support team. Mental health clinicians must have experience working with law enforcement officers for best results. Training for clinicians should be provided to best work with LEO’s and first responders. This is especially true for officers who self-refer. Clinical hours should be supervised by the police consulting psychologist.
Police Stress Intervention Continuum: An empirical option for LEO’s and command staff to reduce officer suicide
Scope of the Problem: Police Suicide and the goal to eliminate it – modified December 28, 2022
Police job-related stress is well-identified and reported in the media daily and the rates of suicide nationwide are being debated by Aamodt and Stalnaker. They are actually less than one is led to believe but even one law enforcement officer suicide is too much. During the week of Christmas 2022, 3 police officers took their own lives at Chicago PD. Some law enforcement officer deaths may be reduced by using a stress intervention continuum. This ties the continuum of calls into a stress reduction protocol that empowers resilience and recognizes the importance of stress mentoring and the soft hand-off for defusing the growing impact of high stress and high lethality exposure. The stress intervention continuum does not single out one officer but identifies all officers – including call takers, dispatchers, and supervisors for defusing particularly abhorrent events like mass shootings. This way, personnel who played a roll in a “bad call” will not be overlooked nor stigmatized for stress reduction defusing and/or debriefing.
Stress is defined as any situation that negatively impacts an officer’s well-being. The rate of suicide and divorce among law enforcement is approximately the same or lower than the general public according to a meta-analysis conducted by Professor Michael Aamodt. But there are areas in the country and agencies that have higher rates of self-inflicted death.
When the suicide rate of police officers (18.1) is compared with the 21.89 rate for a comparable demographic population, it appears that police officers have a lower rate of suicide than the population according to Aamodt, 2008.
Incidence of suicide tend to be elevated in cities like Chicago, where chronic gun violence and a murder rate in the hundreds per year means cops see a staggering amount of traumatic events. As a result, they may gradually become numb to the exposure of pain and suffering (Joyner, 2009). A Department of Justice report found that the suicide rate in the Chicago Police Department is 60 percent higher than the national average. According to the 2018 Chicago Sun Times, in a note to department members, former CPD Supt. Eddie Johnson said in 2018, “Death by suicide is clearly a problem in Law Enforcement and in the Chicago Police Department. We all have our breaking points, a time of weakness where we feel as if there is no way out, no alternative. But it does not have to end that way. You are NOT alone. Death by suicide is a problem that we can eliminate together” CST September 12, 2018. Chicago PD is not alone with the problem of suicide among its men and women in blue. In fact, smaller departments with fewer than 50 officers often have high rates of suicide and lack the peer support and clinical resources that enable officers to find help during times of crisis.
Law enforcement officers (LEO’s) encounter the worst of all experience on a routine basis. The people who call the police may be society’s best upstanding citizens but on this occasion it could be the worst day of their lives and they seek help from police. Many times it is not the pillars of society seeking help but those people in the fringes or margins of society now victims of violent crime or abuse.
According to Hartley, et.al., 2007, “repeated exposures to acute work stressors (e.g., violent criminal acts, sad and disturbing situations, and physically demanding responses), in addition to contending with negative life events (e.g., divorce, serious family or personal illness, and financial difficulties), can affect both the psychological and physiological well-being of the LEO population.” When these officers are identified there needs to be a planned response using a peer support infrastructure that provides for a continuum of service depending upon the individual needs of the LEO and the supports available. In many agencies, especially smaller departments lacking resources, officers’ languish and sometimes spiral downward without support and without somewhere to turn. Police officers must have support available to them long before they are expressing suicidal urges.
As programs are identified and service continuum grows the risk of peer conflict over perceived betrayal of trust must be addressed. This must be addressed in the peer support training with emphasis on preservation of life over maintenance of confidentiality or the status quo of abject silence. “In itself, it’s a product of centuries of police culture in which perceived weakness is stigmatized. Cops know their brothers have their back, no matter what, but they still don’t want to be seen as the one who’s vulnerable.” according to a recent Men’s Health article written by Jack Crosbie in a report about suicide in the NYPD published during Mental Health Awareness month in May 2018.
The argument is made that the recurring uncertainty of police calls for service often leave LEO’s with low-level exposure to trauma of varying degrees. It is common that LEO’s move from one violent call to the next without time to decompress and process what they have seen. The repeated exposure to trauma can slowly whittle away LEO resilience – defined as the capacity to bounce back from adversity. In a national media study published by Aamodt and Stalnaker, legal problems were a major reason for the law enforcement suicides yet no other study separately cited legal problems. In another study, relationship problems accounted for the highest percentage of suicides at 26.6% (relationship problems plus murder/suicide), followed by legal problems at 14.8%. In nearly a third of the suicides, no reason was known for LEO suicide.
Police suicide has been on the radar of advocates of LEO peer support for months or years. The incidence of suicide has remained stable across the country but some agencies have higher rates of suicide. Smaller departments – those with less than 50 officers in general have the highest rates of suicide. This may be linked to the lack of availability of peer support programs and a paucity of local practitioners to provide professional service with knowledge in police psychology. “While police officers may adapt to the negative effects of chronic stress, acute traumatic incidents necessitate specialized mental health treatment for police officers (Patterson, 2001)”. A referral to the department EAP often falls flat and makes it more difficult to make the hand-off when peer support is not enough.
Points of entry to Peer Support – Stress Intervention Continuum
- Exposure to highly stressful events in close sequence
- Change in work assignment, district/station, deployment undercover or return from deployment
- Increased absenteeism – over use of sick leave – missing court dates
- Increased use/abuse of substances – impacting job functioning, on-the-job injury
- Community – citizen complaint(s) for verbal abuse, dereliction of duty, vehicle crash
- Citizen complaints of excessive force during arrest, supervisory or peer conflict, or direct insubordination
- Abuse of power using baton, taser or firearm, recurrent officer involved use of force. Officers are sometimes strongly embittered and angry at this point in their career due to perceived lack of support and powerful feelings career disappointment and alienation – copyright Michael Sefton, Ph.D.
Real-time model of change
The use of force continuum is well described in the LEO literature and ongoing criminal justice narrative. What does that have to do with stress intervention in police officers? It sets the tone for officer behavior whenever they meet potential resistance and or increased aggression during citizen encounters. It may also be used for initiating peer support needs whenever an incident use of force has occurred. LEO’s change the force response based on the situation they encounter in real-time in a flexible and fluid manner. In this same way, peer support programs can flexibly shift to the needs of a presenting LEO and intervene early on – rather than when an officer is at a breaking point. “This continuum (use of force) has many levels, and officers are instructed to respond with a level of force appropriate to the situation at hand, acknowledging that the officer may move from one point on the continuum to another in a matter of seconds.” NIJ publication. Peer support too, must accommodate a law enforcement officer in real-time to begin the process of building a healthy, resilient response to sometimes horrific exposures and provide a continuum of unbiased employee assistance and when necessary professional consultation.
Protective Factors begin in Academy training
What topics should addressed while LEO recruits are in training? Ostensibly, the resilience of LEO’s depends upon the opportunity for in-service training in topics of mindfulness, stress management, physical health maintenance, nutrition, and trust.
“Emotional resilience is defined as the capacity to integrate the breadth of police training and experience with healthy, adaptive coping, optimism, mental flexibility and healthy resolution of the traumatic events. In general, resilient people are self-reliant and have positive role models from whom they have learned to handle the stressful events all police officers encounter” according to Leo Polizoti, Ph.D. a police consulting psychologist (Sefton 2018).
Police programs for health maintenance
The Police Stress Intervention Continuum or P-SIC, involves a system of police support that varies in its intensity depending upon the continuum of individual needs of the LEO including physical debility or other significant components impacting career success and satisfaction. The intervention protocol is flexible and fluid as well. The entry point into the peer support continuum initiates from supervisory observations of LEO history and behavior, peer recommendations, and exposure to a range of traumatic events.
The cumulative stress associated with a career in law enforcement cannot be understated. In the setting of police stress and stress support there is an intervention protocol that relates to the peer-support program continuum. Depending on where officers enter the peer support network will impact the level of intervention they may require in the P-SIC program. Peer support is not psychotherapy but officers occasionally must hand off the officer in trouble to a higher level of care. These hand-offs are key to linking at-risk LEO’s with range of professional support needed to keep them on the job. Yet fear of reprisal for acknowledging the cumulative impact of stress and its impact often derails the hand-off to the professional. The highest risk for suicide to a LEO is when he is denuded of badge and gun because he may be a threat to himself.
The career success they have may be directly related to the application of resiliency training to build and maintain physical and emotional hardiness that lasts a lifetime according to Leo Polizoti, 2018. Before this can happen the stigma associated with reaching out must be reduced.
NIJ Publication (2009). Use of Force Continuum. https://www.nij.gov/topics/law-enforcement/officer-safety/use-of-force/Pages/continuum.aspx. Taken November 17, 2018
Aamodt, M. G., & Stalnaker, N. A. (2001). Police officer suicide: Frequency and officer profiles. In Shehan, D. C, & Warren, J. I. (Eds.) Suicide and Law Enforcement. Washington, D.C.: Federal Bureau of Investigation.
Aamodt, M. (2008). Reducing Misconceptions and False Beliefs in Police and Criminal Psychology. Criminal Justice and Behavior 2008; 35; 1231 DOI: 10.1177/0093854808321527.
Patterson, G T. (200l). Reconceptualizing traumatic incidents experienced by law enforcement personnel. The Australian Journal of Disaster and Trauma Studies, 2.
Joyner, T. (2009) The Interpersonal-Psychological Theory of Suicidal Behavior: Current Empirical Status. Science Briefs, American Psychological Association, June.
Sefton, M. (2018). Police Training: Revisiting Resilience Blog post: https://msefton.wordpress.com/2018/07/27/police-training-revisiting-resilience/. Taken November 18, 2018
Sefton, M. (2018) Points of Entry to Peer Support and mentoring. Blog post: https://wordpress.com/post/msefton.blog/5269 – taken December 27, 2022
Hartley, T., et.al.(2007). Associations Between Major Life Events, Traumatic Incidents, and Depression Among Buffalo Police Officers. International Journal of Emergency Mental Health, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp.
John M. Violanti, Anna Mnatsakanova, Tara A. Hartley, Michael E. Andrew, Cecil M. Burchfiel. (2012). Police Suicide in Small Departments: A comparative analysis. Int J Emerg Ment Health. Author manuscript available in PMC 2015 Aug 14. Published in final edited form as: Int J Emerg Ment Health. 2012; 14(3): 157–162.
What is driving the killing: Update on the Myth of Mental Illness
After a spate of bomb threats and mass shootings there are still many myths about the attribution of these events and the underpinnings of violence. The knee jerk reaction is to attribute the recent Thousand Oaks, CA nightclub shooting to a “crazed gunman” but that would unfairly place the blame on the mentally ill. 12 people were left dead in a despicable sequence of events during which the shooter Ian David Long posted that he had no reason for doing it except boredom. In truth, most people with mental illness are not dangerous, and most dangerous people are not mentally ill.” Liza Gold, 2013. But Long had a history of violence and aggressive behavior that may have been linked to his service as a decorated US Marine. Published information suggests Long’s mother was terrified of making him angry out of fear that he would harm or kill her. Was Long’s terminal behavior attributable to mental illness or the result of traumatic events he experienced in the service of his country?
“Fact is I had no reason to do it, and I just thought….(expletive), life is boring so why not?” Ian David Long via social media post (now removed)
Psychological experts believe mentally ill persons lack the higher order planning to execute the complex steps necessary for anything more than petty crime – more often associated with co-morbid substance abuse. It is the co-occuring illness of drug or alcohol addiction that is a confounding variable in all police-mental health encounters. “Doctors and scientists know that the perpetrators of such violent behavior including incidence mass shooting events are frequently angry young men, who feel they have been mistreated by society and therefore seek to exact revenge” described in a BBC the report Criminal Myths published in November.

“Confounding variables such as a history of childhood abuse or use of alcohol or drugs can increase the odds of violence.” according to a BBC report debunking the belief that people who commit mass murder are mentally ill by Rachel Newer in November, 2018. The vast majority of cases are committed by a person or persons without mental illness. In fact, people with mental illness are more likely to be victims of crime and are not prone to violent behavior. The Thousand Oaks killer refused any mental health support and was not driven by demons
The interaction of substance abuse and mental illness is complex. Persons with drug and alcohol addiction must be expected to become sober with the help of substance abuse treatment and family support. The risk of violence and suicide declines when sobriety can be maintained. This is essential and will help to reduce officer involved use of force against the mentally ill substantially. What to do?
Red flag indicators are often demonstrated in behaviors that are observable and measurable sometimes for weeks and months before the terminal event according to Michael Sefton, 2015.
The incidence of mental illness leading to mass shooting may be illustrated in the 2007 Virginia Tech shootings. The Virginia Tech shooter Seung-Hui Cho had been treated for depression and was hospitalized on an involuntary basis prior to the rampage in 2007. Cho exhibited a life-long pattern of withdrawal from interpersonal relationships. He was often nonverbal and did not respond to people who reached out to him including direct family members. His mother prayed for God to transform her son.
I strongly believe that mental illness does not mitigate citizens from responsibility for crimes they commit. I agree that alternative sentencing may be a powerful tool to bring these individuals into treatment. The substantive goal of streamlining encounters between police officers and citizens who suffer with untreated emotional problems belies the mission of these gifted officers and can teach others the role of discretion in mental health encounters.
Ostensibly, building relationships with network psychotherapists, physicians, addiction specialists, court judges, and other support service like Child and Family Services is essential. This is the area of most vulnerability. When LEO’s fully buy-in to the mental health – police intervention model including the use of de-escalation techniques there must be receiving facilities available to initiate treatment and keep patients and citizens safe. The development of a fully integrated infrastructure for jail diversion, intake, and providing for the needs of the mentally ill is certainly a work in progress.